In today’s world, we’re all looking for ways to be...
In hospitals the concept of sustainability is transcending from a mere trend to an imperative. Hospitals, as bastions of healing and hope, are increasingly recognizing their responsibility not only to treat patients, but also to care for the environment. The design and operation of healthcare facilities play a crucial role in shaping the well-being of patients, staff, and the planet alike. In this era of heightened environmental awareness, the notion of sustainable hospital design has emerged as a beacon of progress. It encompasses a multifaceted approach that seeks to harmonize the healing needs of patients with the ecological imperatives of our time
By integrating eco-friendly strategies into the planning, construction, and operation of hospitals, we can create facilities that not only promote healing but also mitigate their environmental footprint. In this blog, we will discuss the realm of sustainable hospital design, exploring innovative strategies and best practices aimed at fostering healing environments while safeguarding the planet. Each aspect of design contributes to a holistic vision of healthcare that prioritizes both human health and environmental sustainability
The Importance of Sustainable Hospital Design
Before delving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to understand why sustainable hospital design matters. Traditional hospital buildings often consume large amounts of energy and water, generate substantial waste, and emit harmful pollutants. By contrast, hospitals aim to minimize these negative impacts while promoting environmental, economic, and social well-being. Here’s why it’s essential:

1. Environmental Impact Reduction
By implementing energy-efficient systems, hospitals can significantly decrease their energy consumption, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, strategies such as natural light integration and the use of renewable energy sources contribute to further energy conservation.Imperishable design practices also prioritize waste reduction and recycling initiatives, diverting a significant portion of waste from landfills. By minimizing waste generation, hospitals can mitigate their environmental footprint while also setting an example for sustainable practices in the healthcare industry
2. Improved Patient Outcomes
Integrating green spaces, maximizing natural light, and improving air quality are essential components that directly impact patient well-being and recovery. Research has consistently shown that exposure to nature and access to green spaces have positive effects on mental health, stress reduction, and overall well-being. Similarly, natural light not only creates a more pleasant environment but also regulates circadian rhythms, improving sleep patterns and promoting faster healing. Improving indoor air quality with ventilation and low-emission materials promotes a healthier environment for patient healing, lowering the risk of airborne infections and respiratory problems
3. Cost Savings
Energy-efficient designs and the integration of renewable energy sources offer substantial cost-saving opportunities for hospitals over the lifespan of their buildings. By implementing energy-efficient systems such as LED lighting, high-efficiency HVAC systems, and smart building automation, hospitals can significantly reduce their energy consumption and operational expenses. One can also incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal heating and cooling systems further decreasing reliance on grid-based electricity and fossil fuels. Overall, investing in energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies proves to be a financially prudent decision for healthcare facilities
4. Community Health and Resilience
Hospitals promote community health by implementing eco-friendly practices that reduce pollution. These hospitals minimize emissions through energy efficiency and waste reduction, improving air and water quality for nearby residents. By conserving resources like water and energy, they lessen the strain on local ecosystems and reduce environmental impact. Furthermore, hospitals prioritize occupant health by enhancing indoor air quality, natural light access, and green spaces, which can boost patient recovery and staff productivity. Embracing sustainability, hospitals fulfill their healthcare mission while advocating for community health and environmental stewardship
Innovative Eco-Friendly Strategies for Sustainable Hospital Design
Designing hospitals with sustainability in mind is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and promoting the well-being of patients, staff, and the community. Here are some innovative eco-friendly strategies for sustainable hospital design:
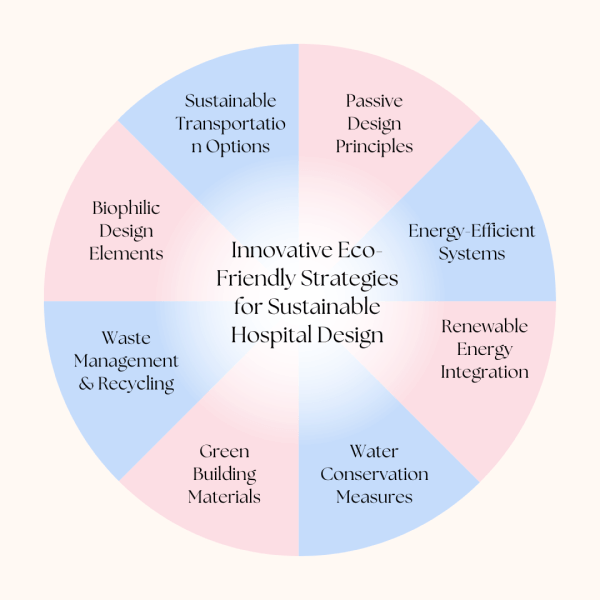
1. Passive Design Principles
Incorporating passive design principles such as orientation, natural ventilation, and daylighting can indeed significantly reduce energy consumption in hospital buildings. By strategically orienting buildings to maximize natural light exposure and harness prevailing winds, hospitals can minimize reliance on artificial lighting and mechanical ventilation systems. This decreases energy usage and enhances indoor air quality and occupant comfort. Eco-friendly strategies for healthcare settings such as shading devices, thermal mass, and high-performance glazing further optimize energy efficiency by reducing heat gain and loss, thus lowering the demand for heating and cooling. Overall, integrating passive design principles into hospital architecture offers a holistic approach to energy efficiency, promoting sustainability
2. Energy-Efficient Systems
Implementing energy-efficient systems, lighting fixtures, and appliances offers significant reductions in energy consumption and operating costs. Technologies such as LED lighting, high-efficiency HVAC units, and occupancy sensors are not only smarter hospital facility designs but play a pivotal role in optimizing energy usage without compromising comfort or functionality. LED lighting, for instance, consumes far less energy than traditional lighting sources while providing superior illumination. Similarly, high-efficiency HVAC systems utilize advanced controls and variable-speed technologies to deliver precise temperature regulation while minimizing energy waste.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems represents a pivotal step towards sustainability. By harnessing the power of nature, hospitals can offset energy demand and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental conservation. Installing solar panels on rooftops or parking structures allows hospitals to generate clean energy onsite, supplementing traditional grid power with renewable electricity. Similarly, wind turbines and geothermal systems can provide additional renewable energy sources, further diversifying the hospital’s energy portfolio. Beyond reducing environmental impact, integrating renewable energy sources enhances the resilience of hospitals, ensuring continued operation during power outages and disruptions
4. Water Conservation Measures
Adopting water-efficient fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling technologies is paramount to minimize water consumption and alleviate strain on local water resources. Incorporating low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads drastically reduces water usage without compromising functionality or user experience. Rainwater harvesting systems allow hospitals to capture and store rainwater for non-potable uses such as landscape irrigation and toilet flushing, further reducing reliance on municipal water supplies. Furthermore, greywater recycling technologies treat wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry facilities, converting it into reusable water for non-potable purposes
5. Green Building Materials
Choosing building materials with low embodied energy, recycled content, and non-toxic properties can enhance indoor air quality and reduce environmental impact. Options for materials such as bamboo, recycled steel, and reclaimed wood offer viable alternatives to conventional construction materials that often come with a significant environmental footprint. Bamboo, known for its rapid growth and renewability, serves as an eco-friendly substitute for hardwoods in flooring and millwork. Recycled steel minimizes the need for new resources and reduces waste, making it an eco-friendly option for structural elements. Reclaimed wood sourced from salvaged buildings or responsibly managed forests provides a rustic aesthetic while preserving valuable resources
6. Waste Management Recycling
Implementing comprehensive waste management and recycling programs within hospitals is crucial for diverting significant amounts of waste from landfills and promoting environmental sustainability. By adopting eco-friendly strategies to create for innovative in hospital design, hospitals can minimize their environmental footprint and contribute to a circular economy. Source separation involves segregating different types of waste at the point of generation, making it easier to recycle materials such as paper, plastics, glass, and metals. Composting organic waste, including food scraps and yard trimmings, not only reduces landfill methane emissions but also produces nutrient-rich compost for landscaping and gardening purposes
7. Biophilic Design Elements
Incorporating biophilic design elements, such as green roofs, indoor plants, and healing gardens, into hospital environments can profoundly enhance the connection between patients, staff, and nature. These features serve to beautify the space and offer a range of tangible benefits for occupants. Green roofs, for instance, provide natural insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and mitigate the urban heat island effect, while also creating habitats for wildlife. Indoor plants have been shown to improve indoor air quality by filtering out pollutants and increasing oxygen levels, thereby promoting better respiratory health and overall well-being. Also, healing gardens offer tranquil outdoor spaces where patients, staff, and visitors can connect with nature, reducing stress, boosting mood, and facilitating healing
8. Sustainable Transportation Options
Encouraging sustainable transportation options for patients, staff, and visitors is paramount for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and alleviating traffic congestion around hospitals. By providing amenities such as bike racks, electric vehicle charging stations, and convenient access to public transit, hospitals can promote alternative modes of transportation and support broader sustainability goals. Bike racks encourage cycling as a clean and healthy means of transportation, reducing reliance on cars and promoting physical activity. Electric vehicle charging stations accommodate the growing number of electric vehicles on the road, incentivizing drivers to choose cleaner, more eco-friendly transportation options.
Design Sustainable Hospitals With Experts
Designing a hospital requires a holistic approach that encompasses energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction, and biophilic design principles. By incorporating innovative eco-friendly strategies into the design, we can create environments that promote healing, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to the well-being of communities and the planet. But we need professional hands for this, and consulting Inner Value Architects can provide valuable insights and expertise. As we continue to prioritize sustainability in healthcare infrastructure, we move closer to a future where hospitals not only treat illnesses but also serve as models of environmental stewardship and resilience