In today’s world, we’re all looking for ways to be...
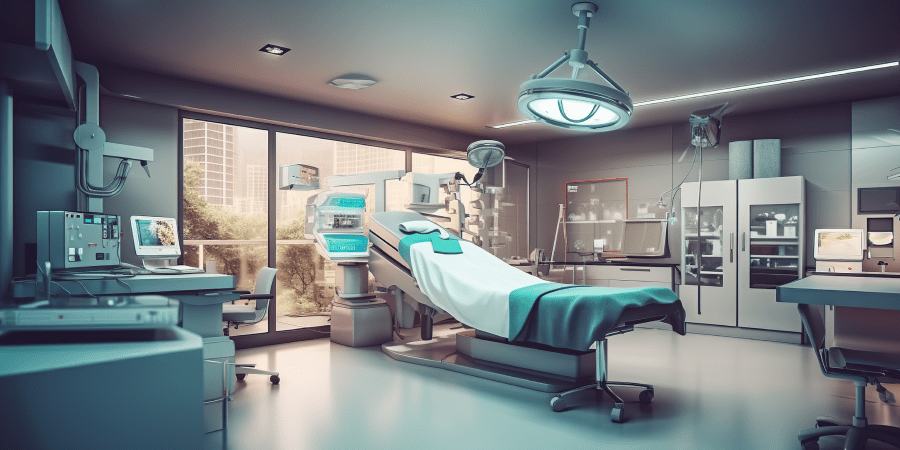
Hospital emergency departments (EDs) stand as the frontline of healthcare, where critical moments define patient outcomes. Traditionally, these environments have been synonymous with stress, overcrowding, and inefficiency, prompting a revolutionary shift in their architectural design. Today, architects and healthcare professionals are collaboratively reimagining EDs to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and elevate the overall healthcare experience.
This blog delves into the transformative innovations shaping modern ED architecture. By exploring these innovative approaches, we uncover how forward-thinking design can profoundly impact patient outcomes and pave the way for the future of emergency healthcare. Join us as we delve into the future of emergency department design and discover how thoughtful architecture is playing a crucial role in saving lives and improving healthcare outcomes.
Ways to Create Modern Hospital Emergency Departments
Creating modern hospital emergency departments (EDs) involves architects integrating design principles that enhance functionality, patient experience, and operational efficiency. Here’s how architects can achieve this:
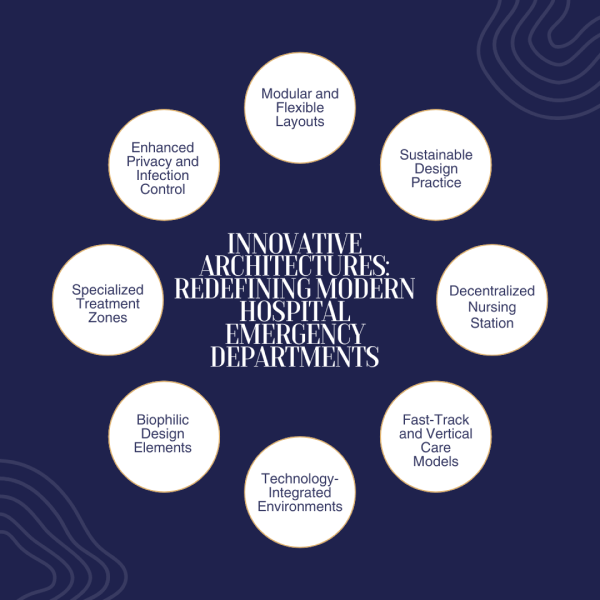
1. Modular and Flexible Layouts
Modern ED (Emergency Departments) designs are moving away from rigid, fixed layouts towards more adaptable spaces. Today architects have many options, they can create modular environments that feature movable walls and reconfigurable treatment areas, allowing for swift adjustments based on specific patients care needs. This adaptability optimizes workflow and enhances the overall efficiency of patient care delivery. Also modular design can facilitate quick transformations, creating additional beds or specialized treatment zones as required. Flexibility enables emergency departments to respond dynamically to the ever-changing demands of healthcare, ensuring timely and effective patient care.
2. Sustainable Design Practices
Sustainable designs are not only good for the environment but also enhance the health and well-being of patients and staff. Architects should design sustainable hospitals and create buildings that utilize energy-efficient systems, such as LED lighting and advanced HVAC technologies, to significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs. Incorporating sustainable materials, like recycled and locally sourced products, can further decrease the facility’s ecological footprint. Architects should create designs that support natural ventilation and maximizing daylight to improve indoor air quality and create a more uplifting environment.
3. Decentralized Nursing Stations
When designing emergency departments, architects should revolutionize patient care by implementing decentralized nursing stations. In modern hospital architecture design architects should place nursing stations throughout the ED rather than in a centralized location. By Decentralizing nursing station hospitals can enhance staff visibility and accessibility, allowing nurses to be closer to patients at all times. This design idea fosters improved communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, leading to more efficient workflows and quicker response times. With nurses positioned nearer to those in need, you create a supportive environment that prioritizes patient safety and satisfaction.
4. Fast-Track and Vertical Care Models
Innovative strategies like fast-track and vertical care models are essential for enhancing efficiency and patient flow in emergency departments. Architects should create spaces that support these models to improve the overall functionality of the ED. Designing dedicated fast-track areas can add maximum comfort and accessibility for patients with minor injuries or non-urgent conditions and can significantly reduce wait times and alleviate congestion in the main treatment zones. These areas should be easily accessible and equipped with the necessary medical supplies to handle quick assessments and treatments. Incorporating vertical care models allows for treating patients in an upright position, optimizing space and streamlining care for ambulatory patients.
5. Technology-Integrated Environments
Smart technologies are transforming healthcare environments by enhancing connectivity, improving patient care, and streamlining operations. When designing modern emergency departments, architects should create technology-integrated environments that leverage these innovations to optimize both the patient experience and staff workflows. By incorporating advanced technologies, you enable seamless communication among healthcare teams and improve decision-making processes. Embracing technology, architects can create an environment that supports clinical excellence and fosters a more responsive and streamlined experience for patients and providers alike.
6. Biophilic Design Elements
Biophilic design elements focus on incorporating natural elements into built environments to enhance the physical and emotional well-being of the occupants. Research has shown that exposure to nature can reduce stress, improve mood, and accelerate healing. To create modern emergency departments, architects should integrate biophilic design principles. By designing spaces that feature abundant natural light, green spaces, and the use of natural materials, you can significantly enhance the healing environment. Incorporate indoor gardens or green walls brings the tranquility of nature indoors, creating a soothing atmosphere. Using natural materials like wood and stone can add warmth and an inviting feel to the space.
7. Specialized Treatment Zones
Specialized treatment zones in emergency departments are designed to cater to specific medical needs, enhancing both the efficiency of care delivery and patient outcomes. By segmenting the ED into distinct areas for trauma, pediatrics, mental health, and minor injuries, healthcare providers can offer more targeted and effective treatments. For implementation, architects should create specialized treatment zones within emergency departments. To create adaptable space for changing medical center needs, architects should design a trauma zone equipped with advanced life-support technology. A pediatric area with child-friendly designs and equipment can help reduce anxiety and provide a comforting environment for young patients. Mental health zones, designed with calming colors, soft lighting, and privacy considerations, can offer a safe and therapeutic space for patients experiencing psychological distress.
8. Enhanced Privacy and Infection Control
Enhanced privacy and infection control are crucial for maintaining patient confidentiality, reducing stress, and preventing the spread of infections within the hospital setting. To address these needs effectively, architects should create environments that prioritize both privacy and stringent infection control measures. By designing private treatment rooms with soundproofing and visual barriers, you can ensure that patient conversations and examinations remain confidential, thus enhancing patient comfort and trust. Additionally, implementing dedicated isolation areas with negative pressure ventilation is vital for containing infectious diseases and protecting other patients and staff. Using easy-to-clean materials and surfaces throughout the ED, along with strategically placed hand hygiene stations, can further minimize the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
Create Emergency Departments With Experts
The evolution of emergency department design is pivotal in enhancing patient care, improving operational efficiency, and fostering healing environments. By embracing innovative strategies architects can create spaces that truly respond to the needs of patients and healthcare providers alike. As you embark on the journey of designing or renovating an emergency department, consider consulting Inner Value Architects for expert guidance and support. Their commitment to creating thoughtful, functional, and sustainable healthcare environments will help you achieve your vision for a modern emergency department that meets the demands of today’s healthcare landscape.